Department of Chemical Biology
Yang's Lab,Department of Chemical Biology, Xiamen University
Professor Yang
 Know more>>
Professor
Department of Chemical Biology, Xiamen University
Know more>>
Professor
Department of Chemical Biology, Xiamen University
Contact Information
Yang's LaboratoryRoom 532, Lujiaxi Building, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
Ph: +86 (0) 592-218 7601cyyang@xmu.edu.cn
Mengjiao Huang's paper accepted by Anal. Chem.
2019-07-29 01:55:34

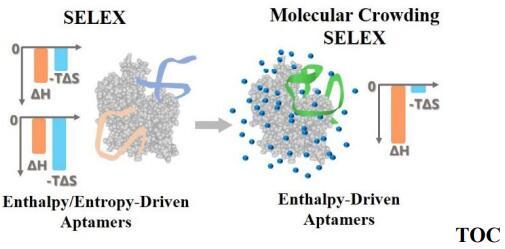
An enthalpy-driven ligand is an ideal probe for practical applications because of the formation of abundant specific bonds between the ligand and target, compared to an entropy-driven ligand with a similar Gibbs free energy change. However, there has been a lack of direct discovery strategy for identifying enthalpy-driven ligands. In this work, a Molecular Crowding SELEX strategy for discovering enthalpy-driven aptamers was developed to improve the affinity and selectivity of aptamers in complex samples. Three aptamer sequences were successfully evolved against a tumor biomarker protein and all proved to be enthalpy-driven by thermodynamics analysis, establishing the feasibility of Molecular Crowding SELEX for effective discovery of enthalpy-driven aptamers. Further comparison of aptamers evolved from conventional SELEX in buffer and Molecular Crowding SELEX (SYL-H2C) revealed much higher affinity of SYL-H2C. With its improved thermodynamic properties, the enthalpy-driven SYL-H2C aptamer was able to detect circulating tumor cells in real cancer patient blood samples with excellent detection accuracy (10/10). The proposed molecular crowding screening strategy offers a promising direction for discovering robust binding probes for a great variety of biomedical applications.