Professor Yang
 Know more>>
Professor
Department of Chemical Biology, Xiamen University
Know more>>
Professor
Department of Chemical Biology, Xiamen University
Contact Information
Yang's LaboratoryRoom 532, Lujiaxi Building, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
Ph: +86 (0) 592-218 7601cyyang@xmu.edu.cn
Review Article by Lingling Wu has been accepted by ACS Applied Bio Materials.
2020-02-25 14:49:55

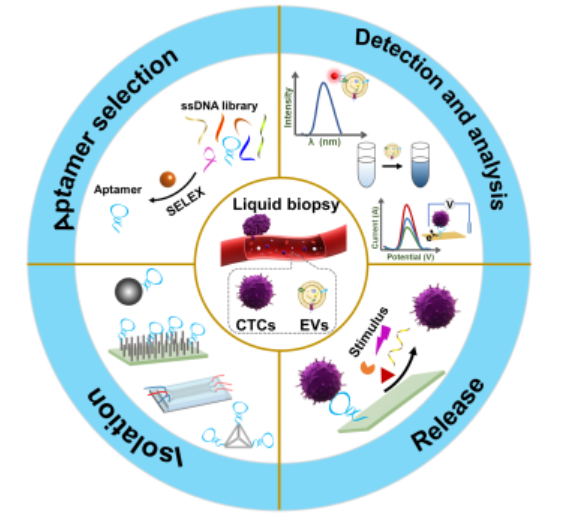
Liquid biopsy allows noninvasive and real-time analysis of tumor-derived circulating targets in body fluids, holding great value for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, personalized therapy, as well as the understanding of mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis and progression. However, the low concentration and heterogeneity of circulating targets and the complexity of body fluids bring daunting technical challenges to liquid biopsy. Aptamers with many unique properties are considered as promising recognition ligands for liquid biopsy. Their facile modification and affinity regulation afford numerous platforms for efficient isolation and release of circulating targets. With versatile structural design and engineering, aptamers also offer many strategies for sensitive detection and analysis of circulating targets. In this review, recent progress in aptamer-based liquid biopsy is summarized, with a focus on the isolation and detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and extracellular vesicles (EVs). First, recent emerged strategies for evolving aptamers against circulating targets are introduced, and existing aptamers successfully applied in liquid biopsy are comprehensively summarized including their targets, sequences, affinities, etc. Then, aptamer-based approaches for CTC isolation, release, and analysis are summarized. Additionally, aptamer-mediated signal transduction and amplification for the detection of EVs are also reviewed. Finally, the challenges and future perspectives in this field are discussed.