Department of Chemical Biology
Yang's Lab,Department of Chemical Biology, Xiamen University
Professor Yang
 Know more>>
Professor
Department of Chemical Biology, Xiamen University
Know more>>
Professor
Department of Chemical Biology, Xiamen University
Contact Information
Yang's LaboratoryRoom 532, Lujiaxi Building, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
Ph: +86 (0) 592-218 7601cyyang@xmu.edu.cn
Jingjing Guo's paper has been accepted by Lab Chip
2020-03-07 13:59:03

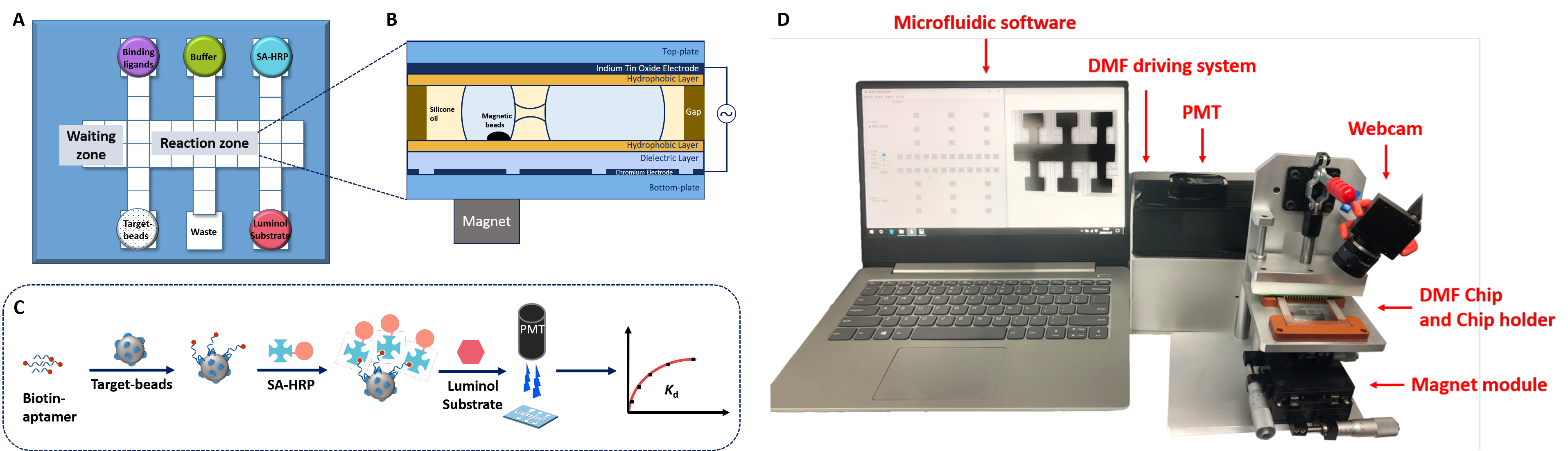
The dissociation constant (Kd) is a crucial parameter for characterizing binding affinity of molecular recognition, including antigen-antibody, DNA-protein, and receptor-ligand interactions. However, conventional methods for Kd characterization usually involve a multi-step process and time-consuming operations for incubation, washing, and detection, thus causing problems, such as time delays, microbead loss, degradation of sensitive molecules, and personal error. Here we demonstrate an automated ligand binding affinity evaluation platform (Auto-affitech) using digital microfluidics (DMF), with individual droplets at the microliter level programmed to rapidly perform the incubation and separation of target-beads and binding ligands. Because the loss of the beads influences the detection results, we propose a new strategy for magnetic bead separation on DMF, termed the bidirectional separation method. By splitting one droplet into two asymmetric droplets, high bead retention efficiency (89.57%±0.05%) and high washing efficiency (99.59%±0.17%, with four washings) were obtained. We demonstrate the determination of Kd of an aptamer-protein system (EpCAM and its corresponding aptamer SYL3C) and an antigen-antibody system (H5N1 antigen and antibody), proving the capability and the universality of Auto-affitech in various receptor-ligand systems. Integrating all the sample processing procedures, the Auto-affitech not only saves manual labor and minimizes personal errors, but also conserves sample and shortens analysis time. Overall, this platform successfully demonstrates an automated approach to dissociation constant evaluation and exhibits great potential for highly efficient screening of ligands.